Configure Sandbox
We recommend completing the following steps to prepare your Braintree Sandbox Account to connect to your reader and to gain foundational knowledge before your Dev Kit arrives.
1. Create a Braintree Sandbox Account
The Dev Kit Verifone P400 reader is designed to be used only with one Braintree Sandbox Account. Once it is paired to a Braintree Sandbox Account the reader cannot be used with any other Braintree Sandbox Account. Please take some time to create a Braintree Sandbox Account or log in to your existing Braintree Sandbox Account.
2. Review Authentication Options
Review the API Authentication Options to determine and implement your merchant authentication method of choice. Whether you are a developer working directly with a Merchant or a third-party integrator working on behalf of a Merchant, you will need to choose the implementation that best suits your use case.
The fastest way to get up and running will be using the static 1st-party API Keys. These two values (Public Key and Private Key) are generated inside your Braintree sandbox merchant account and should be copied and saved in a safe place for future use.
3. Make a Braintree GraphQL Request
To get up and running quickly we recommend using the Postman API Client in conjunction with the Braintree GraphQL - In-Store Postman Collection.
After importing the collection to Postman, be sure to update the
collection settings to use your Braintree sandbox credentials. To do that,
click on the collection, select the Authorization tab, change
Type
to
Basic Auth, enter your sandbox Public API Key into the
Username field and Private Key into the Password field, and click Save.
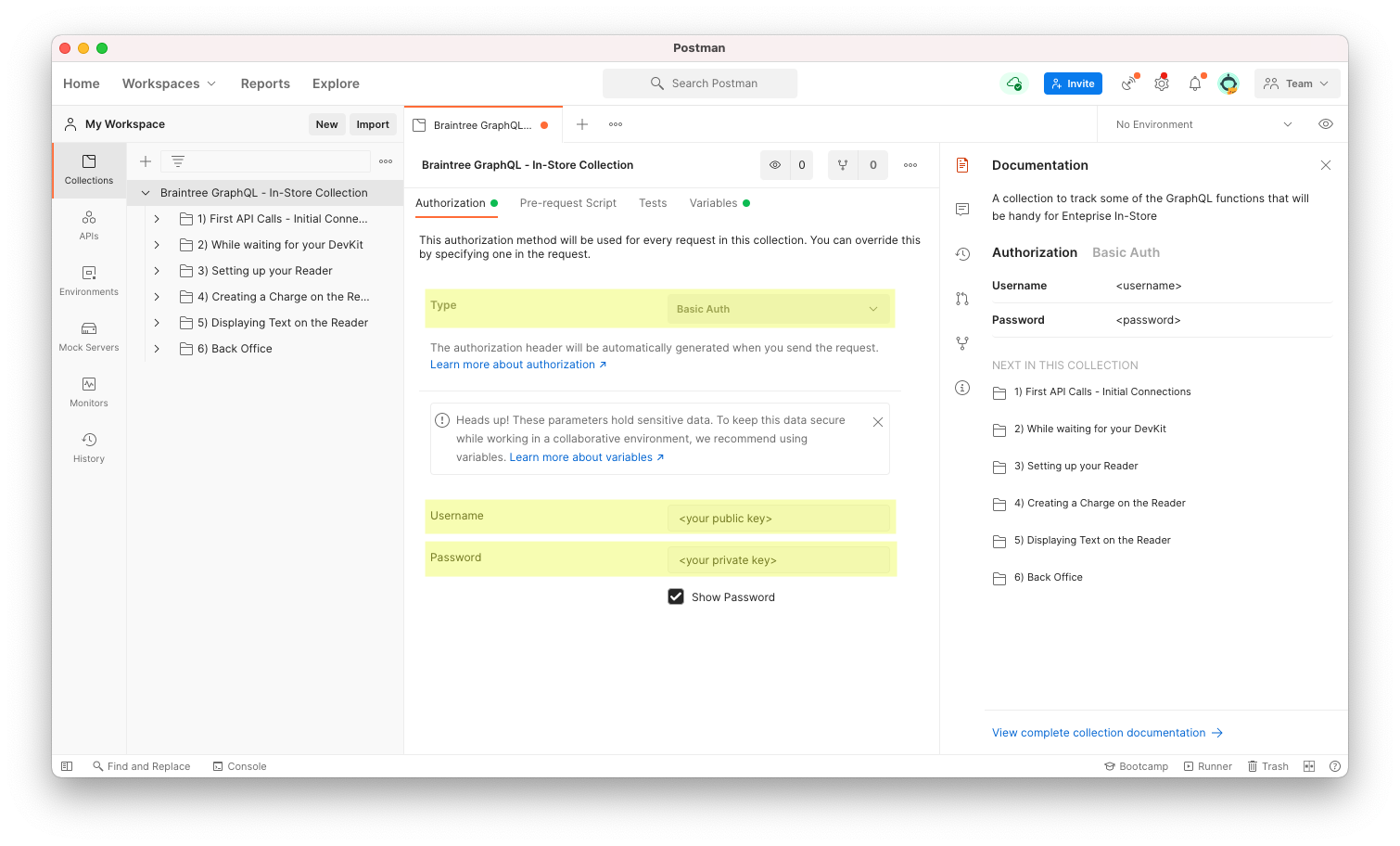
Make your first Braintree GraphQL API request to ensure connectivity. Learn more about creating your own API requests and options available to you.
4. Configure Custom Fields in Sandbox (Optional)
Optionally, you may configure In-Store specific custom fields if required on your sandbox merchant account. Custom fields allow you to save additional In-Person specific payment data with each transaction for visibility in the control panel and for reporting purposes. For example, a Cashier ID or tracking the employee that created the transaction.
5. Test a "card not present" transaction
Test creating a card not present transaction using GraphQL and a range of the testing nonce values.
6. Implement reversals
After you've charged a payment method, you might want to test how to cancel the transaction or refund the customer's money later. Follow this guide on How to Reverse or Refund a Transaction using the test transactions created in the previous step. You can also find some Auth Reversal GraphQL API examples in our Gitbook documentation.
7. Search for transactions
The search query returns the fields you can use to search for objects. Review and test making transaction searches for any back-office or reporting needs. You can also find some GraphQL API examples for using a transaction query in our Gitbook documentation.